 vscode插件开发
vscode插件开发
# 创建项目
安装依赖
pnpm i -g yo generate-code
初始化插件目录
yo code
注:如果报错:You don't seem to have a generator with the name “generator-code” installed. 就先执行npm install generator-code.
# 目录结构
{
"name": "i18n-automatically", // 定义了插件的包名,它必须是唯一的并且符合 npm 的包命名规范。
"displayName": "I18n Automatically", // 定义了插件在 Visual Studio Code 中显示的名称。
"description": "vscode国际化多语言自动生成替换方案",
"version": "0.0.1",
"engines": {
"vscode": "^1.92.0" // 定义了插件所支持的 Visual Studio Code 的最低版本。
},
"categories": [ // 定义了插件所属的分类,以便在 Visual Studio Code 中组织和展示插件。
"Extension Packs",
"Programming Languages",
"Visualization",
"Debuggers",
"Notebooks"
],
"activationEvents": [], // 定义了激活插件的事件
"main": "./out/extension.js", // 定义插件的入口文件
"contributes": {
"commands": [
{
"command": "i18n-automatically.mytest", // 注册的插件命令
"title": "mytest"
}
]
},
"scripts": {
"vscode:prepublish": "npm run compile",
"compile": "tsc -p ./",
"watch": "tsc -watch -p ./",
"pretest": "npm run compile && npm run lint",
"lint": "eslint src --ext ts",
"test": "node ./out/test/runTest.js",
"prepare": "husky install",
"commitlint": "commitlint --config commitlint.config.js -e -V"
},
"devDependencies": {},
"lint-staged": {
"**/*": "prettier --write --ignore-unknown"
}
}
# 运行插件
F5 运行插件 vsode会打开一个新的调试窗口
在新的调试窗口中,按 ctrl + shift + p,打开命令面板;
输入注册的插件命令,即可执行插件。 在package.json和extension文件中定义了命令,项目的默认命令是hello word,可自行更改。
# 功能实现
extension.ts作为项目的入口文件,里面的两个函数定义了插件激活/销毁时要执行的功能:
// 模块“vscode”包含VS Code可扩展性API
// 导入模块,并在下面的代码中使用别名vscode引用它
const vscode = require("vscode");
// 当您的扩展被激活时,会调用此方法
// 您的扩展在第一次执行命令时被激活
/**
* @param {vscode.ExtensionContext} context
*/
function activate(context) {
// 使用控制台输出诊断信息(console.log)和错误(console.error)
// 当您的扩展被激活时,这行代码只会执行一次
console.log(
'Congratulations, your extension "i18n-automatically" is now active!'
);
// 该命令已在package.json文件中定义
// 现在使用registerCommand提供命令的实现
// commandId参数必须与package.json中的命令字段匹配
const disposable = vscode.commands.registerCommand(
"i18n-automatically.helloWorld",
function () {
// The code you place here will be executed every time your command is executed
// Display a message box to the user
vscode.window.showInformationMessage(
"Hello World from i18n-automatically!"
);
}
);
context.subscriptions.push(disposable);
}
// This method is called when your extension is deactivated
function deactivate() {}
module.exports = {
// 插件激活
activate,
// 插件销毁
deactivate,
};
剩下的开发和平时一样。
# 打包发布
# 账号准备
https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage (opens new window)
# package.json修改
新增 publisher: publisher ID
# 打包命令
安装依赖
pnpm i @vscode/vsce -g
打包,在根目录下执行打包命令,执行成功后,会在根目录下生成 .vsix 文件
用yarn的话,后面加参数
vsce package --yarn
# 发布
- 命令发布
vsce publish -p YOUR_PUBLISHER_ID
# 参考链接
https://rackar.github.io/vscode-ext-doccn/ (opens new window)
# 原理讲解( AST 自动转换国际化方案分享)
# 1. 整体思路
# 1.1. 技术选型
Vue SFC 解析: @vue/compiler-sfc
- 用于解析 .vue 文件的模板和脚本部分
- 分别处理 template、script、scriptSetup 块
Babel 工具链:
const parser = require('@babel/parser'); // 将代码解析为 AST const traverse = require('@babel/traverse'); // 遍历和修改 AST const t = require('@babel/types'); // AST 节点类型处理 const generate = require('@babel/generator'); // AST 转回代码
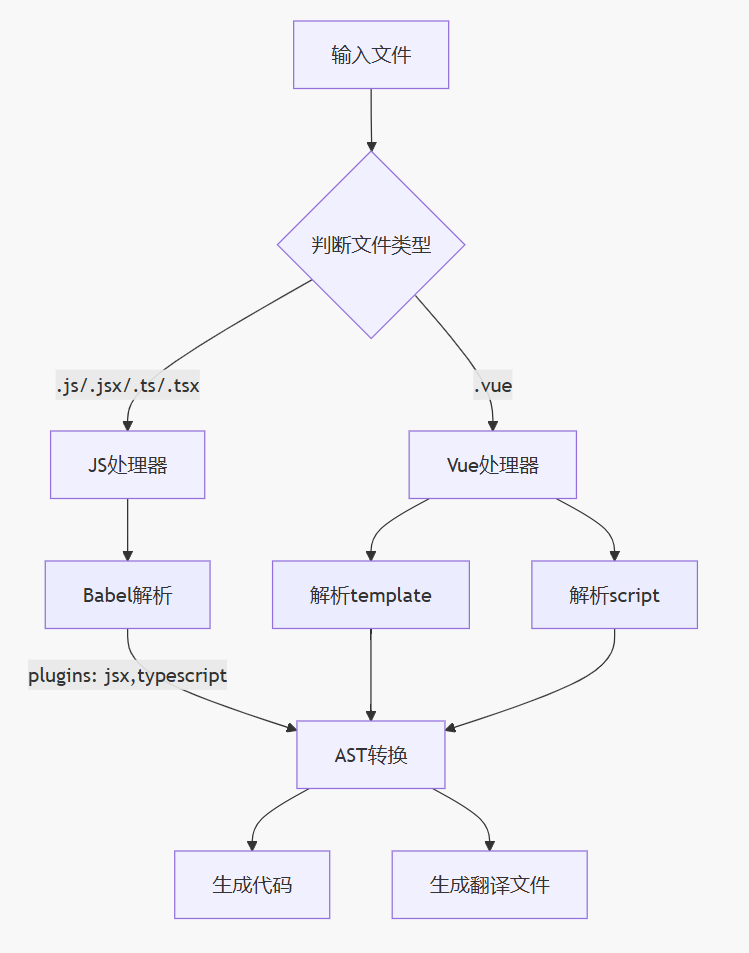
# 2. 支持的文件类型
# 2.1. Vue 单文件组件 (.vue)
// 文件处理器
function getFileProcessor(fileExt) {
const processors = {
'.vue': handleVueFile, // Vue 处理器
...
};
}
// Vue 文件解析
async function handleVueFile(filePath, config) {
const { descriptor } = parseSfc(fileContent);
// 1. 处理模板
if (descriptor.template) {
processTemplate(descriptor.template.ast);
}
// 2. 处理脚本
if (descriptor.script) {
processScript(descriptor.script.content);
}
// 3. 处理 setup
if (descriptor.scriptSetup) {
processScript(descriptor.scriptSetup.content);
}
}
# 2.2. JavaScript/TypeScript 文件
const processors = {
'.js': handleJsFile, // JavaScript
'.jsx': handleJsFile, // React JSX
'.ts': handleJsFile, // TypeScript
'.tsx': handleJsFile, // React TSX
};
# 2.3. 解析配置
// Babel 解析配置
const parseOptions = {
sourceType: 'module',
plugins: [
'jsx', // 支持 JSX 语法
'typescript', // 支持 TypeScript
'decorators-legacy', // 支持装饰器
],
};
// Vue 解析配置
const vueOptions = {
filename: 'component.vue',
sourceMap: false,
};
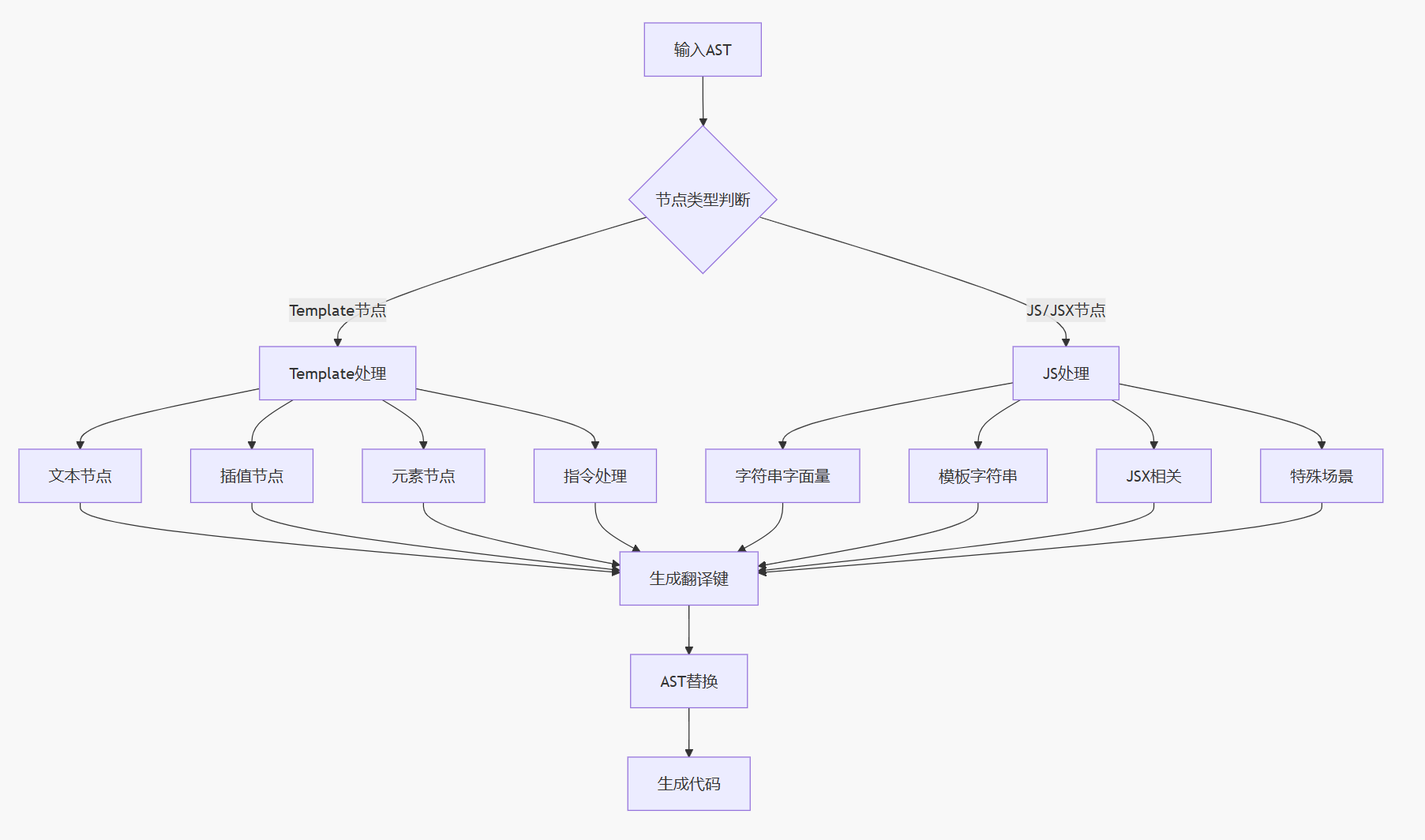
# 3. AST 转换核心处理
# 核心工作流程
# 3.1. Template AST 转换
# 3.1.1. 节点类型处理
// 处理不同类型的模板节点
function processTemplate(templateAst, context) {
const nodeTypeHandlers = {
// 注释节点
3: (node) => node.loc.source,
// 文本节点 - 处理纯文本内容
2: (node) => {
if (containsChinese(node.content)) {
const key = generateKey(context);
context.translations.set(key, node.content.trim());
return `{{ $t('${key}') }}`;
}
return node.content;
},
// 插值节点 - 处理 {{ }} 内的表达式
5: (node) => {
if (node.content.ast) {
// 处理包含 JS 表达式的插值
return processInterpolationNode(node, context);
}
return processTemplateString(node.content.content, context);
},
// 元素节点 - 处理标签及其属性
1: (node) => processElementNode(node, context),
};
return astArrayToTemplate(templateAst, nodeHandlers);
}
# 3.1.2. 元素节点处理
function processElementNode(node, context) {
let result = `<${node.tag}`;
// 处理属性
if (node.props) {
for (const prop of node.props) {
// 处理指令 (v-bind, v-on 等)
if (prop.type === 7) {
result += processDirective(prop, context);
}
// 处理普通属性
else if (prop.type === 6) {
result += processAttribute(prop, context);
}
}
}
// 处理子节点
if (!node.isSelfClosing) {
result += '>';
if (node.children) {
result += node.children
.map((child) => astToTemplate(child, context))
.join('');
}
result += `</${node.tag}>`;
} else {
result += ' />';
}
return result;
}
# 3.1.3. 指令处理
function processDirective(prop, context) {
const name = getDirectiveName(prop);
// 没有表达式的指令
if (!prop.exp) return `\n${name}`;
// 处理带表达式的指令
if (containsChinese(prop.exp.content)) {
// 处理包含 HTML 的情况
if (stringWithDom(prop.exp.content)) {
const handlerContent = prop.exp.content
.trim()
.replace(/^[\s\n]*[`'"]|[`'"][\s\n]*$/gm, '');
const result = handlerDomNode(handlerContent, context);
return `\n${name}="\`${replaceForI18nCall(result, context)}\`"`;
}
// 处理普通中文表达式
const result = handlerForJs(prop.exp, context);
return `\n${name}="${replaceForI18nCall(result, context)}"`;
}
return `\n${name}="${prop.exp.content}"`;
}
# 3.2. JavaScript AST 转换
# 3.2.1. AST 遍历处理
function processJsAst(context) {
const ast = parser.parse(context.contentSource, {
sourceType: 'module',
plugins: ['jsx', 'typescript', 'decorators-legacy'],
});
traverse(ast, {
// 处理字符串字面量
StringLiteral(path) {
handleChineseString(path, context);
},
// 处理模板字符串
TemplateElement(path) {
handleChineseString(path, context, true);
},
// 处理 JSX 文本
JSXText(path) {
handleChineseString(path, context);
},
// 处理 JSX 属性
JSXAttribute(path) {
handleJSXAttribute(path, context);
},
// 处理 JSX 表达式容器
JSXExpressionContainer(path) {
handleJSXExpressionContainer(path, context);
},
// 处理程序入口,检查 i18n 导入
Program: {
enter(path) {
checkForI18nImport(path, context);
},
},
});
return generateCode(ast, context);
}
# 3.2.2. 中文字符串处理
function handleChineseString(path, context, isTemplateLiteral = false) {
try {
const value = isTemplateLiteral ? path.node.value.raw : path.node.value;
// 跳过非中文或调试上下文
if (!containsChinese(value) || isInDebugContext(path)) return;
// 处理包含 HTML 的字符串
if (stringWithDom(value)) {
handleStringWithDom(path, context, isTemplateLiteral);
return;
}
const key = generateKey(context);
// 根据不同场景选择替换策略
if (isTemplateLiteral) {
handleTemplateLiteral(path, context, key);
}
// JSX 场景
else if (path.type === 'JSXText' || path.parent?.type.includes('JSX')) {
replaceWithJSXI18nCall(path, context, key);
}
// 普通字符串场景
else {
replaceWithI18nCall(path, context, key);
}
// 保存翻译
context.translations.set(key, value.trim());
} catch (error) {
context.index--;
customConsole.error('handleChineseString 错误:', error);
}
}
# 3.2.3. 特殊场景处理
// 处理带 HTML 的字符串
function handleStringWithDom(path, context, isTemplateLiteral) {
if (path.type === 'StringLiteral') {
convertStringLiteralToTemplateLiteral(path, context);
} else if (isTemplateLiteral) {
processTemplateElement(path, context);
}
}
// 处理模板字符串
function handleTemplateLiteral(path, context, key) {
const templateLiteral = path.parentPath;
const newExpression = t.callExpression(
t.identifier(context.config.scriptI18nCall),
[t.stringLiteral(key)],
);
// 保持原有表达式的顺序
const existingExpressions = templateLiteral.node.expressions.map((exp) => ({
node: exp,
start: exp.start,
}));
existingExpressions.push({
node: newExpression,
start: path.node.start,
});
// 重新排序并更新节点
templateLiteral.node.expressions = existingExpressions
.sort((a, b) => a.start - b.start)
.map((item) => item.node);
}
// 上下文检查
function isInDebugContext(path) {
const debugContexts = [
// 检查 console 调用
(p) =>
p.isCallExpression() &&
p.get('callee').isMemberExpression() &&
p.get('callee.object').isIdentifier({ name: 'console' }),
// 检查 Error 抛出
(p) =>
p.isNewExpression() && p.get('callee').isIdentifier({ name: 'Error' }),
// 检查断言
(p) =>
p.isCallExpression() && p.get('callee').isIdentifier({ name: 'assert' }),
// 检查调试器语句
(p) => p.isDebuggerStatement(),
];
return debugContexts.some((context) => path.findParent(context));
}
# 处理模板字符串,为什么要重新排序?
- 模板字符串的结构:
// 一个模板字符串可能包含多个表达式,例如:
`Hello ${name}, your score is ${score}!`;
- 在 AST 中,这个模板字符串被表示为:
- quasis(静态文本部分):["Hello ", ", your score is ", "!"]
- expressions(表达式):[name, score]
- 当我们在处理国际化时,可能会遇到这样的情况:
`用户 ${name} 的分数是 ${score} 分`;
- 处理后我们希望变成:
`${t('user-key')} ${name} ${t('score-key')} ${score} ${t('point-key')}`;
需要排序的原因:
- AST 遍历过程中可能不是按照代码中的顺序处理表达式的
- 当我们添加新的 i18n 函数调用时,需要确保它们被插入到正确的位置
- expressions 数组中表达式的顺序必须与模板字符串中出现的顺序完全匹配
来看一个具体例子:
// 原始代码
`用户 ${name} 的分数是 ${score} 分`
// AST处理过程中可能的顺序:
1. 处理 "用户"
2. 处理 "的分数是"
3. 处理 "分"
// 如果不排序,可能会变成:
`${t('point-key')} ${t('user-key')} ${name} ${t('score-key')} ${score}`
// 排序后,正确的顺序:
`${t('user-key')} ${name} ${t('score-key')} ${score} ${t('point-key')}`
通过使用 start 位置进行排序,我们可以确保表达式按照它们在原始代码中出现的顺序排列,从而保持模板字符串的语义不变。这对于保持代码的正确性和可读性都是至关重要的。
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2025/03/17, 12:21:00
