 深浅拷贝
深浅拷贝
浅拷贝只拷贝一层对象,如果有对象的嵌套就要用深拷贝,也就是彻底的拷贝
# 浅拷贝方法
# 手动实现
const shallowClone = (target) => {
if (typeof target === "object" && target !== null) {
const cloneTarget = Array.isArray(target) ? [] : {};
for (let prop in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = target[prop];
}
}
return cloneTarget;
} else {
return target;
}
};
精简一下,去掉判断,改为 Object.keys
const shallowClone = (target) => {
if (typeof target === "object" && target !== null) {
const cloneTarget = Array.isArray(target) ? [] : {};
for (let prop in Object.keys(target)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = target[prop];
}
return cloneTarget;
} else {
return target;
}
};
# Object.assign
Object.assgin() 拷贝的是对象的属性的引用,而不是对象本身。
let obj = { name: "shenzjd.com", age: 18 };
const obj2 = Object.assign({}, obj, { name: "blog.shenzjd.com" });
console.log(obj2); // {name: "blog.shenzjd.com", age: 18}
# concat
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
let newArr = arr.concat();
newArr[1] = 100;
console.log(arr); // [1,2,3]
# slice
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
let newArr = arr.slice();
newArr[1] = 100;
console.log(arr); // [1,2,3]
# 展开运算符
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
let newArr = [...arr];
newArr[1] = 100;
console.log(arr); // [1,2,3]
# 深拷贝
# JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())
能覆盖大部分场景,但是严格意义上来说,有如下问题
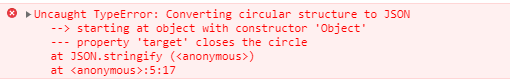
- 无法解决循环引用
const a = { val: 2 };
a.target = a;
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(a));
拷贝 a 会出现系统栈溢出,因为出现了无限递归的情况
- 无法拷贝特殊的对象: RegExp,Date,Set,Map 等
- 无法拷贝函数
# 简易版深拷贝
const deepClone = (target) => {
if (typeof target === "object" && target !== null) {
const cloneTarget = Array.isArray(target) ? [] : {};
for (let prop in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = deepClone(target[prop]); // 浅拷贝没有递归,只有一层
}
}
return cloneTarget;
} else {
return target;
}
};
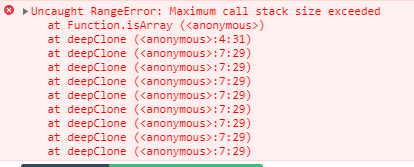
# 解决循环引用
let a = { val: 100 };
a.target = a;
deepClone(a);
创建一个 Map。记录下已经拷贝过的对象,如果说已经拷贝过,那直接返回它
const isObject = (target) => {
(typeof target === "object" || typeof target === "function") &&
target !== null;
};
const deepClone = (target, map = new Map()) => {
if (map.get(target)) return target;
if (isObject(target)) {
map.set(target, true);
const cloneTarget = Array.isArray(target) ? [] : {};
for (let prop in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = deepClone(target[prop]); // 浅拷贝没有递归,只有一层
}
}
return cloneTarget;
} else {
return target;
}
};
测试
let a = { val: 100 };
a.target = a;
deepClone(a);

好像是没有问题了, 拷贝也完成了。但还是有一个潜在的坑, 就是 map 上的 key 和 map 构成了强引用关系,这是相当危险的。我给你解释一下与之相对的弱引用的概念你就明白了:
在计算机程序设计中,弱引用与强引用相对, 是指不能确保其引用的对象不会被垃圾回收器回收的引用。 一个对象若只被弱引用所引用,则被认为是不可访问(或弱可访问)的,并因此可能在任何时刻被回收。 --百度百科
被弱引用的对象可以在任何时候被回收,而对于强引用来说,只要这个强引用还在,那么对象无法被回收
拿上面的例子说,map 和 a 一直是强引用的关系, 在程序结束之前,a 所占的内存空间一直不会被释放。
怎么解决这个问题?
很简单,让 map 的 key 和 map 构成弱引用即可。ES6 给我们提供了这样的数据结构,它的名字叫 WeakMap,它是一种特殊的 Map, 其中的键是弱引用的。其键必须是对象,而值可以是任意的。
稍微改造一下即可:
const deepClone = (target, map = new WeakMap()) => {
//...
};
# 拷贝特殊对象
用 Object.prototype.toString.call()判断
可遍历对象
["object Map"];
["object Set"];
["object Array"];
["object Object"];
["object Arguments"];
const getType = Object.prototype.toString.call(obj);
const canTraverse = {
"[object Map]": true,
"[object Set]": true,
"[object Array]": true,
"[object Object]": true,
"[object Arguments]": true,
};
const isObject = (target) => {
(typeof target === "object" || typeof target === "function") &&
target !== null;
};
const deepClone = (target, map = new WeakMap()) => {
if (!isObject(target)) return target;
let type = getType(target);
let cloneTarget;
if (!canTraverse[type]) {
// 这里处理不能遍历的对象
return;
} else {
// 这波操作相当关键,可以保证对象的原型不丢失!
let ctor = target.prototype;
cloneTarget = new ctor();
}
if (map.get(target)) return target;
map.put(target, true);
// 处理Map
if (type === mapTag) {
target.forEach(item, (key) => {
cloneTarget.set(deepClone(key), deepClone(item));
});
}
// 处理 Set
if (type === setTag) {
target.forEach((item) => {
target.add(deepClone(item));
});
}
// 处理数组和对象
for (let prop in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = deepClone(target[prop]);
}
}
return cloneTarget;
};
不可遍历的对象
const boolTag = "[object Boolean]";
const numberTag = "[object Number]";
const stringTag = "[object String]";
const dateTag = "[object Date]";
const errorTag = "[object Error]";
const regexpTag = "[object RegExp]";
const funcTag = "[object Function]";
对于不可遍历的对象,不同的对象有不同的处理
const handleRegExp = (target) => {
const { source, flags } = target;
return new target.constructor(source, flags);
};
const handleFunc = (target) => {
// 待会的重点部分
};
const handleNotTraverse = (target, tag) => {
const Ctor = targe.constructor;
switch (tag) {
case boolTag:
case numberTag:
case stringTag:
case errorTag:
case dateTag:
return new Ctor(target);
case regexpTag:
return handleRegExp(target);
case funcTag:
return handleFunc(target);
default:
return new Ctor(target);
}
};
# 拷贝函数
函数分为两种,每个普通函数都是 Function 的实例,而箭头函数不是任何类的实例,每次调用都是不一样的引用
- 普通函数
- 箭头函数
这里只需要处理普通函数,箭头函数直接返回他本身就可以
怎么区分
利用原型,箭头函数没有原型
const handleFunc = (func) => {
// 箭头函数直接返回自身
if (!func.prototype) return func;
const bodyReg = /(?<={)(.|\n)+(?=})/m;
const paramReg = /(?<=\().+(?=\)\s+{)/;
const funcString = func.toString();
// 分别匹配 函数参数 和 函数体
const param = paramReg.exec(funcString);
const body = bodyReg.exec(funcString);
if (!body) return null;
if (param) {
const paramArr = param[0].split(",");
return new Function(...paramArr, body[0]);
} else {
return new Function(body[0]);
}
};
# bug
const target = new Boolean(false);
const Ctor = target.constructor;
new Ctor(target); // 结果为 Boolean {true} 而不是 false
对于这样一个 bug,我们可以对 Boolean 拷贝做最简单的修改, 调用 valueOf: new target.constructor(target.valueOf())
但实际上,这种写法是不推荐的。因为在 ES6 后不推荐使用【new 基本类型()】这 样的语法,所以 es6 中的新类型 Symbol 是不能直接 new 的,只能通过 new Object(SymbelType)
const handleNotTraverse = (target, tag) => {
const Ctor = targe.constructor;
switch (tag) {
case boolTag:
return new Object(Boolean.prototype.valueOf.call(target));
case numberTag:
return new Object(Number.prototype.valueOf.call(target));
case stringTag:
return new Object(String.prototype.valueOf.call(target));
case errorTag:
case dateTag:
return new Ctor(target);
case regexpTag:
return handleRegExp(target);
case funcTag:
return handleFunc(target);
default:
return new Ctor(target);
}
};
# 完整的深拷贝
const getType = (obj) => Object.prototype.toString.call(obj);
const isObject = (target) =>
(typeof target === "object" || typeof target === "function") &&
target !== null;
const canTraverse = {
"[object Map]": true,
"[object Set]": true,
"[object Array]": true,
"[object Object]": true,
"[object Arguments]": true,
};
const mapTag = "[object Map]";
const setTag = "[object Set]";
const boolTag = "[object Boolean]";
const numberTag = "[object Number]";
const stringTag = "[object String]";
const symbolTag = "[object Symbol]";
const dateTag = "[object Date]";
const errorTag = "[object Error]";
const regexpTag = "[object RegExp]";
const funcTag = "[object Function]";
const handleRegExp = (target) => {
const { source, flags } = target;
return new target.constructor(source, flags);
};
const handleFunc = (func) => {
// 箭头函数直接返回自身
if (!func.prototype) return func;
const bodyReg = /(?<={)(.|\n)+(?=})/m;
const paramReg = /(?<=\().+(?=\)\s+{)/;
const funcString = func.toString();
// 分别匹配 函数参数 和 函数体
const param = paramReg.exec(funcString);
const body = bodyReg.exec(funcString);
if (!body) return null;
if (param) {
const paramArr = param[0].split(",");
return new Function(...paramArr, body[0]);
} else {
return new Function(body[0]);
}
};
const handleNotTraverse = (target, tag) => {
const Ctor = target.constructor;
switch (tag) {
case boolTag:
return new Object(Boolean.prototype.valueOf.call(target));
case numberTag:
return new Object(Number.prototype.valueOf.call(target));
case stringTag:
return new Object(String.prototype.valueOf.call(target));
case symbolTag:
return new Object(Symbol.prototype.valueOf.call(target));
case errorTag:
case dateTag:
return new Ctor(target);
case regexpTag:
return handleRegExp(target);
case funcTag:
return handleFunc(target);
default:
return new Ctor(target);
}
};
const deepClone = (target, map = new WeakMap()) => {
if (!isObject(target)) return target;
let type = getType(target);
let cloneTarget;
if (!canTraverse[type]) {
// 处理不能遍历的对象
return handleNotTraverse(target, type);
} else {
// 这波操作相当关键,可以保证对象的原型不丢失!
let ctor = target.constructor;
cloneTarget = new ctor();
}
if (map.get(target)) return target;
map.set(target, true);
if (type === mapTag) {
//处理Map
target.forEach((item, key) => {
cloneTarget.set(deepClone(key, map), deepClone(item, map));
});
}
if (type === setTag) {
//处理Set
target.forEach((item) => {
cloneTarget.add(deepClone(item, map));
});
}
// 处理数组和对象
for (let prop in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = deepClone(target[prop], map);
}
}
return cloneTarget;
};
