 手写基础js
手写基础js
手写一定要重视!!!
- 柯里化
- 深浅拷贝
- 数组扁平化
- 数组去重
- 发布订阅
- 观察者
# 柯里化 curry
const curry = (func, ...args) => {
const fnLen = func.length;
return function (...innerArgs) {
innerArgs = args.concat(innerArgs);
if (innerArgs.length < fnLen) {
return curry(func, ...innerArgs);
} else {
func.apply(this, innerArgs);
}
};
};
const curry2 = (fn) =>
(judge = (...args) =>
args.length >= fn.length
? fn(...args)
: (...arg) => judge(...args, ...arg));
// 上面就是下面的简写
const curry3 = (fn) => {
const judge = (...args) => {
if (args.length >= fn.length) {
return fn(...args);
} else {
return (...arg) => {
return judge(...args, ...arg);
};
}
};
return judge;
};
const add = curry((num1, num2, num3) => {
console.log(num1, num2, num3, num1 + num2 + num3);
});
add(1)(2)(3);
add(1, 2)(3);
add(1, 2, 3);
add(1)(2, 3);
https://juejin.cn/post/6950218916018782245 (opens new window)
# 浅拷贝
const shallowClone = (target) => {
if (typeof target === "object" && target !== null) {
const cloneTarget = Array.isArray(target) ? [] : {};
for (let prop in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = target[prop];
}
}
return cloneTarget;
} else {
return target;
}
};
精简一下,改为Object.keys,去掉判断
const shallowClone = (target) => {
if (typeof target === "object" && target !== null) {
const cloneTarget = Array.isArray(target) ? [] : {};
for (let prop in Object.keys(target)) {
cloneTarget[prop] = target[prop];
}
return cloneTarget;
} else {
return target;
}
};
其次还有Object.assgin和Array.slice()以及展开运算符...
# 深拷贝
const deepClone = (target, hash = new WeakMap()) => {
if (target instanceof RegExp) return new RegExp(target);
if (target instanceof Date) return new Date(target);
if (typeof target !== "object" || target === null) return target;
// 循环引用的情况
if (hash.has(target)) {
return hash.get(target);
}
// new 一个相应的对象
// obj为Array,相当于new Array()
// obj为Object,相当于new Object()
let cloneTarget = new target.constructor();
hash.set(target, true);
for (let key in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
cloneTarget[key] = deepClone(target[key]);
}
}
// 考虑symbol的情况
let symbolObj = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(target);
for (let i = 0; i < sumbolObj.length; i++) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(symbolObj[i])) {
cloneTarget[symbolObj[i]] = deepClone(target[symbolObj[i]], hash);
}
}
return cloneTarget;
};
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/1e2e7dfe3b783/ (opens new window)
# 数组扁平化
# flat
let arr = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, [6]]]];
console.log(arr.flat(infinity));
# 递归
let arr = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, [6]]]];
function flatten(arr) {
let result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (Array.isArray(arr[i])) {
result = result.concat(flatten(arr[i]));
} else {
result.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return result;
}
# reduce 迭代
function flatten(arr) {
return arr.reduce((pre, cur) => {
return pre.concat(Array.iaArray(cur) ? flatten(cur) : cur);
}, []);
}
# 扩展运算符
我们先用数组的 some 方法把数组中仍然是数组的项过滤出来,然后执行 concat 操作,利用 ES6 的展开运算符,将其拼接到原数组中,最后返回原数组
// 只要有一个元素有数组,那么循环继续
while (arr.some(Array.isArray)) {
ary = [].concat(...ary);
}
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/6bc4ef1017adc/ (opens new window)
# 数组去重
# set 去重
unique = (arr) => {
return Array.From(new Set(arr));
};
# for of 性能最高
const unique = (arr) => {
let result = [];
let obj = {};
for (let i of arr) {
if (!obj[i]) {
result.push(i);
obj[i] = 1;
}
}
return result;
};
# filter
const unique = (arr) => {
return arr.filter((item) => {
return arr.indexOf(item, 0) === index;
});
};
# includes
const unique = (arr) => {
const result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (!result.includes(arr[i])) {
result.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return result;
};
# es5 性能最高
const unique = (arr) => {
arr = arr.sort();
let result = [arr[0]];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] !== arr[i - 1] && result.push(arr[i]);
}
return result;
};
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/aa99d2b66d8ac (opens new window)
# 发布订阅
发布订阅模式是一种设计模式,他允许对象间进行松散耦合的联系。发布者不会直接调用订阅者,相反,他们通过事件中心发布消息。
订阅者通过注册事件中心的回调函数,来接收事件中心发布的消息。
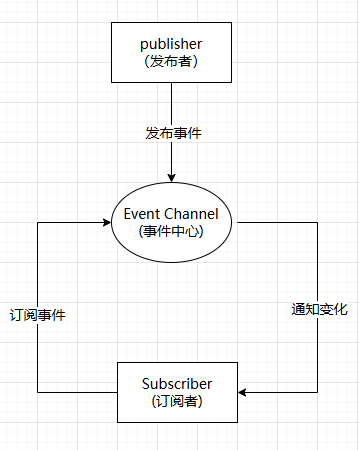
要实现发布订阅模式,我们需要以下几个关键功能
- 一个用于存储事件及回调的存储器
- 一个on方法,用于订阅事件,并将回调函数存储起来
- 一个emit方法,用于发布事件,调用回调函数
- 一个off方法,用于取消订阅事件
class EventEmitter {
constructor() {
this.events = {};
}
// 事件监听
on(eventName, callback) {
if (!this.events[eventName]) {
this.events[eventName] = [];
}
this.events[eventName].push(callback);
return this;
}
// 发布事件
emit(eventName, ...args) {
const callbacks = this.events[eventName] || [];
callbacks.forEach((cb) => cb.call(this, ...args));
return this;
}
// 删除订阅
off(eventName, callback) {
// 啥都没传,所有的事件都取消
if (typeof eventName === "undefined") {
delete this.events;
} else if (typeof eventName === "string") {
// 删除指定事件的回调
if (typeof callback === "function") {
this.events[eventName] = this.events[eventName].filter(
(cb) => cb !== callback
);
} else {
// 删除整个事件
delete this.events[eventName];
}
}
return this;
}
// 只进行一次的事件订阅
once(eventName, callback, context) {
const proxyCallback = (...args) => {
callback.call(context, ...args);
// 回调函数执行完成之后就删除事件订阅
this.off(eventName, proxyCallback);
};
this.on(eventName, proxyCallback, context);
}
}
// 测试
const e1 = new EventEmitter();
const e1Callback1 = (name, sex) => {
console.log(name, sex, "evt1---callback1");
};
const e1Callback2 = (name, sex) => {
console.log(name, sex, "evt1---callback2");
};
const e1Callback3 = (name, sex) => {
console.log(name, sex, "evt1---callback3");
};
e1.on("evt1", e1Callback1);
e1.on("evt1", e1Callback2);
e1.once("evt1", e1Callback3);
e1.emit("evt1", "神族九帝", "boy");
console.log("------尝试删除e1Callback1------");
e1.off("evt1", e1Callback1);
e1.emit("evt1", "神族九帝", "boy");
# 实现一个 compose 函数
// 用法如下:
function fn1(x) {
return x + 1;
}
function fn2(x) {
return x + 2;
}
function fn3(x) {
return x + 3;
}
function fn4(x) {
return x + 4;
}
const a = compose(fn1, fn2, fn3, fn4);
console.log(a(1)); // 1+4+3+2+1=11
// 就是把函数按倒序执行
function compose(...fn) {
if (!fn.length) return (v) => v;
if (fn.length === 1) return fn[0];
return fn.reduce(
(pre, cur) =>
(...args) =>
// 主要看题目是顺序执行,还是倒序执行
pre(cur(...args))
);
}
# 模拟实现 instanceof
function myInstanceof(left, right) {
//基本数据类型直接返回false
if (typeof left !== "object" || left === null) return false;
//getProtypeOf是Object对象自带的一个方法,能够拿到参数的原型对象
let proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(left);
while (true) {
//查找到尽头,还没找到
if (proto == null) return false;
//找到相同的原型对象
if (proto == right.prototype) return true;
proto = Object.getPrototypeof(proto);
}
}
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/15beed3c2f8d4/#实现-instanceof-功能 (opens new window)
# 多维数组拍平
while (ary.some(Array.isArray)) {
ary = [].concat(...ary);
}
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/6bc4ef1017adc/ (opens new window)
# settimeout 模拟实现 setinterval
function mySetinterVal(cb, delay) {
setTimeout(() => {
cb();
mySetinterVal(cb, delay);
}, delay);
}
mySetinterVal(() => {
console.log(1);
}, 1000);
# setInterval 模拟实现 setTimeout
function mySetTimeout(cb, delay) {
const timer = setInterval(() => {
cb();
clearInterval(timer);
}, delay);
}
mySetTimeout(() => {
console.log(1);
}, 1000);
# 手写 call
Function.prototype.call = function (context, ...args) {
let context = context || window;
context.fn = this;
let res = context.fn(...args);
delete context.fn;
return res;
};
# 手写 apply
Function.prototype.call = function (context, args) {
let context = context || window;
context.fn = this;
let res = context.fn(...args);
delete context.fn;
return res;
};
# 手写 bind
Function.prototype.bind = function (context, ...args) {
if (typeof context !== "function") throw typeError();
let that = this;
let rfn = function () {
that.call(context, ...args, arguments);
};
if (this.prototype) {
rfn.prototype = Object.create(this.prototype);
}
return rfn;
};
# 手写 new
function MyNew(ctor, ...args) {
if (typeof ctor !== "function") throw " ctor must be a function";
let obj = Object.create(ctor.prototype);
// let obj = new Object();
// obj.prototype = Object.create(ctor.prototype);
let res = ctor.call(obj, ...args);
let isObject = typeof res === "object" && res !== null;
let isFunction = typeof res === "function";
return isObject || isFunction ? res : obj;
}
# debounce
function debounce(cb, delay) {
let timer = null;
return (...args) => {
timer && clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
cb.call(this, ...args);
}, delay);
};
}
# throttle
// 定时器
function throttle(cb, delay) {
let timer = null;
return (...args) => {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
cb.call(this, ...args);
timer = null;
}, delay);
}
};
}
// 时间戳
function throttle(cb, delay) {
let startTime = Date.now();
return (...args) => {
let lastTime = Date.now();
if (lastTime - startTime > delay) {
cb.call(this, ...args);
startTime = Date.now();
}
};
}
# 防抖节流双剑合璧版本
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/3c209d1a362c4/#双剑合璧-加强版节流 (opens new window)
function throttle(fn, delay) {
let last = 0,
timer = null;
return function (...args) {
let context = this;
let now = new Date();
if (now - last > delay) {
clearTimeout(timer);
setTimeout(function () {
last = now;
fn.apply(context, args);
}, delay);
} else {
// 这个时候表示时间到了,必须给响应
last = now;
fn.apply(context, args);
}
};
}
# 正则模拟 trim 方法
String.prototype.strim1 = function () {
return this.replace(/(^\s+|\s+$)/g, "");
};
String.prototype.strim2 = function () {
return this.replace(/^\s+(.*?)\s+$/g, "$1");
};
let str = " dsfd ";
console.log(str, 1);
console.log(str.trim(), 2);
console.log(str.strim1(), 3);
console.log(str.strim2(), 4);
# 手机号 3-4-4 分割
const splitMobile = (mobile, format = "-") => {
return String(mobile).replace(/(?=(\d{4})+$)/g, format);
};
console.log(splitMobile(13785241526));
# 手写一个深拷贝
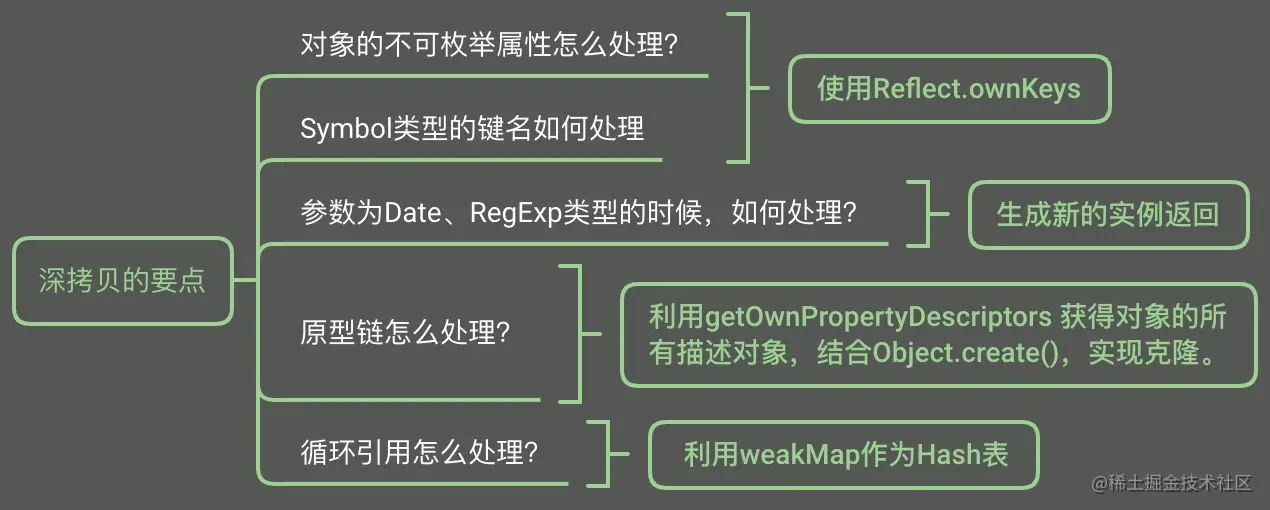
https://juejin.cn/post/6936575075432792094#heading-1 (opens new window)
function deepClone(obj, map = new Map()) {
if (obj instanceof Object) {
if (obj instanceof Function) return obj;
if (obj instanceof Date) return new Date(obj);
if (obj instanceof RegExp) return new RegExp(obj);
// 解决循环引用
if (map.has(obj)) return map.get(obj);
// 拷贝原型链
let allDesc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(target);
let cloneObj = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(target), allDesc);
map.set(obj, cloneObj);
// Reflect.ownKeys可以拿到不可枚举属性和symbol类型的键名
for (let key of Reflect.ownKeys(obj)) {
cloneObj[key] = deepClone(obj[key], map);
}
return cloneObj;
} else {
return obj;
}
}
下面的是完整版深拷贝
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/1e2e7dfe3b783/#完整的深拷贝 (opens new window)
# 千分位格式化数字
const formatPrice = function (num) {
console.log(num);
const [integer, decimal = ""] = String(num).split(".");
console.log(integer, decimal);
return (
integer.replace(/\B(?=(\d{3})+$)/g, ",") + (decimal ? "." + decimal : "")
);
};
console.log(formatPrice(123456789.3343));
# 手写 Object.create
const create = (proto, propertiesObject) => {
// proto 新创建对象的原型对象, propertiesObject 要定义其可枚举属性或修改的属性描述符的对象
if (!["object", "function"].includes(typeof proto)) {
throw new TypeError(
`Object prototype may only be an Object or null: ${proto}`
);
}
// 创建构造函数
const Ctor = function () {};
// 赋值原型
Ctor.prototype = proto;
// 创建实例
const obj = new Ctor();
// 支持第二个参数
if (propertiesObject) {
Object.defineProperties(obj, propertiesObject);
}
// 支持空原型
if (proto === null) {
obj.__proto__ = null;
}
return obj;
};
// 1. object.create常规使用
const person = {
showName() {
console.log(this.name);
},
};
const me = Object.create(person);
const me2 = create(person);
me.name = "神族九帝";
me2.name = "神族九帝";
me.showName();
me2.showName();
// 2. 创建一个原型为null的空对象
const emptyObj = Object.create(null);
const emptyObj2 = create(null);
console.log(emptyObj);
console.log(emptyObj2);
// 3. propertiesObject参数
const propertiesObject = {
// foo会成为所创建对象的数据属性
foo: {
writable: true,
configurable: true,
value: "hello",
},
// bar会成为所创建对象的访问器属性
bar: {
configurable: false,
get: function () {
return 10;
},
set: function (value) {
console.log("Setting `o.bar` to", value);
},
},
};
let o = Object.create(Object.prototype, propertiesObject);
let o2 = create(Object.prototype, propertiesObject);
o.bar = "神族九帝";
o2.bar = "神族九帝";
console.log(o.foo);
console.log(o.bar);
console.log(o2.foo);
console.log(o2.bar);
# 手写 Object.assign
Object.assign = function (target, ...args) {
if (target === null) {
throw new TypeError("cannot convert undefined or null ro Object");
}
// let res = new target.constructor();
let res = Object(target);
args.forEach((item) => {
if (item !== null) {
for (let key in item) {
if (item.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
res[key] = item[key];
}
}
}
});
return res;
};
# 并行控制的 promise
/*
JS实现一个带并发限制的异步调度器Scheduler,保证同时运行的任务最多有两个。完善下面代码的Scheduler类,使以下程序能够正常输出:
class Scheduler {
add(promiseCreator) { ... }
// ...
}
const timeout = time => {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, time)
}
})
const scheduler = new Scheduler()
const addTask = (time,order) => {
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time).then(()=>console.log(order)))
}
addTask(1000, '1')
addTask(500, '2')
addTask(300, '3')
addTask(400, '4')
// output: 2 3 1 4
整个的完整执行流程:
起始1、2两个任务开始执行
500ms时,2任务执行完毕,输出2,任务3开始执行
800ms时,3任务执行完毕,输出3,任务4开始执行
1000ms时,1任务执行完毕,输出1,此时只剩下4任务在执行
1200ms时,4任务执行完毕,输出4
*/
class Scheduler {
constructor() {
this.queue = [];
this.maxCount = 2;
this.runCount = 0;
}
// promiseCreator执行后返回的是一个Promise
add(promiseCreator) {
// 小于等于2,直接执行
this.queue.push(promiseCreator);
this.runQueue();
}
runQueue() {
// 队列中还有任务才会被执行
if (this.queue.length && this.runCount < this.maxCount) {
// 执行先加入队列的函数
const promiseCreator = this.queue.shift();
// 开始执行任务 计数+1
this.runCount += 1;
promiseCreator().then(() => {
// 任务执行完毕,计数-1
this.runCount -= 1;
this.runQueue();
});
}
}
}
const timeout = (time) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(resolve, time);
});
};
const scheduler = new Scheduler();
const addTask = (time, order) => {
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time).then(() => console.log(order)));
};
addTask(1000, "1");
addTask(500, "2");
addTask(300, "3");
addTask(400, "4");
上面的是原题,但是我想实现一个通用的方法
class Scheduler {
constructor(promises, maxCount) {
this.promises = promises;
this.queue = [];
this.maxCount = maxCount;
this.runCount = 0;
this.start();
setTimeout(() => {
this.runQueue();
}, 0);
}
start() {
this.promises.forEach((item) => {
this.queue.push(item);
this.runQueue();
});
}
runQueue() {
if (this.queue.length && this.runCount < this.maxCount) {
const fn = this.queue.shift();
this.runCount++;
fn().then(() => {
this.runCount--;
this.runQueue();
});
}
}
}
const fn1 = () => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(1);
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
};
const fn2 = () => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2);
resolve();
}, 500);
});
};
const fn3 = () => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(3);
resolve();
}, 300);
});
};
const fn4 = () => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(4);
resolve();
}, 400);
});
};
new Scheduler([fn1, fn2, fn3, fn4], 2);
# 手写 JSON.stringify
看一下 MDN 上对规则的描述:

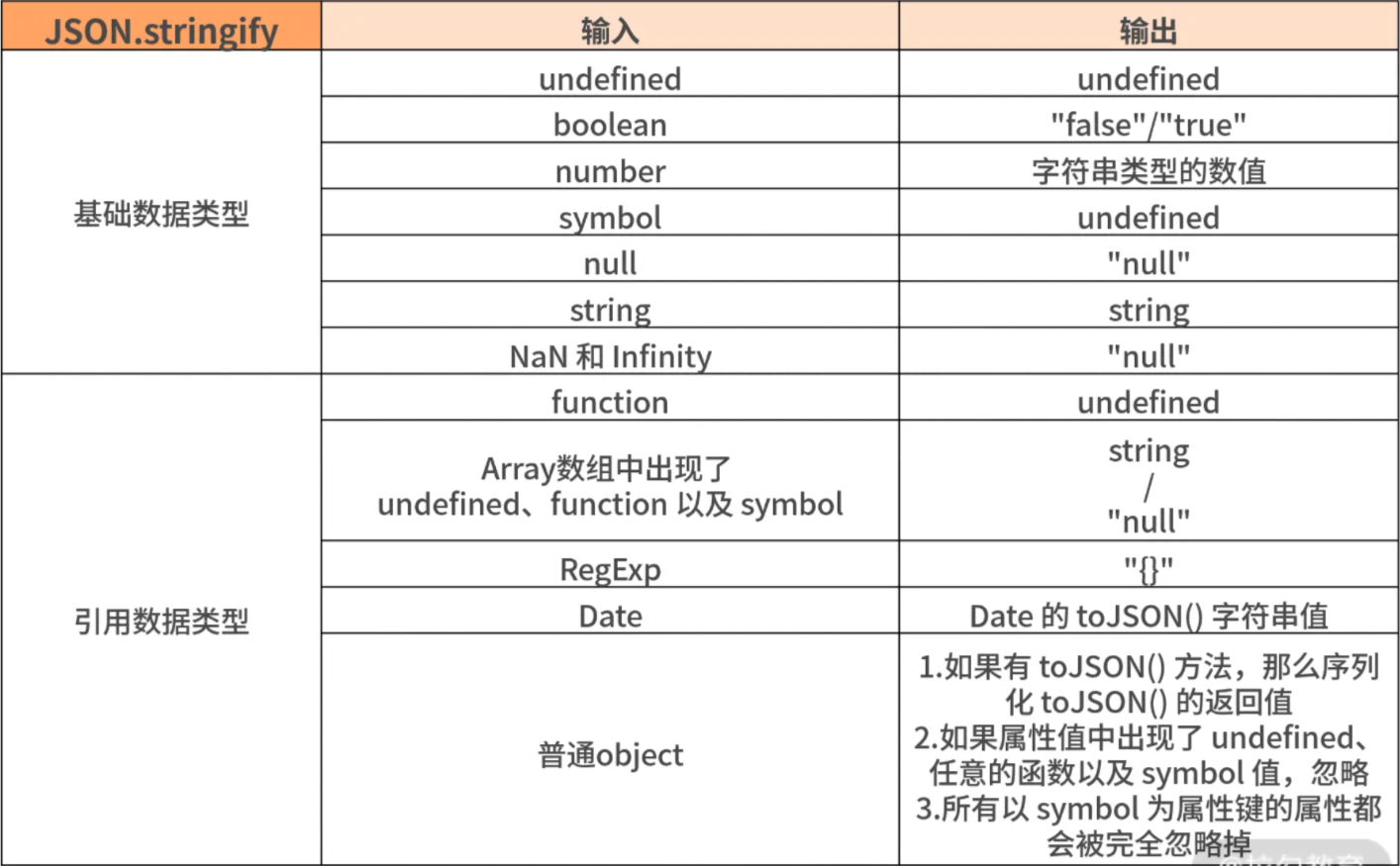
https://juejin.cn/post/6936575075432792094#heading-6 (opens new window)
function jsonStringify(data) {
let result = "";
var type = typeof data;
if (type !== "object" || data === null) {
// 基础类型在此处理
result = data;
if (type == "number" && (Number.isNaN(data) || !Number.isFinite(data))) {
// 规则8:NaN 和 Infinity格式的数值会被当做 null。
result = "null";
} else if (type == "function" || type == "undefined" || type == "symbol") {
// 规则4:函数、undefined 被单独转换时,会返回 undefined,
result = "undefined";
} else if (type == "string") {
result = `"${data}"`;
}
result = String(result);
} else {
if (data.toJSON && typeof data.toJSON == "function") {
//规则1:转换值如果有 toJSON() 方法,该方法定义什么值将被序列化。
result += jsonStringify(data.toJSON());
} else if (data instanceof Array) {
result = [];
data.forEach((item, index) => {
let itemType = typeof item;
// 规则4:undefined、任意的函数以及 symbol 值,出现在数组中时,被转换成 null
if (
itemType == "undefined" ||
itemType == "function" ||
itemType == "symbol"
) {
result[index] = "null";
} else {
result[index] = jsonStringify(item);
}
});
result = `[${result}]`;
} else {
result = [];
Object.keys(data).forEach((item, index) => {
// 规则6:所有以 symbol 为属性键的属性都会被完全忽略掉,Object.keys返回包括对象自身的(不含继承的)所有可枚举属性(不含 Symbol 属性)的键名。
let valueType = typeof data[item];
if (
valueType == "undefined" ||
valueType == "function" ||
valueType == "symbol"
) {
// 规则4:undefined、任意的函数以及 symbol 值,在序列化过程中会被忽略(出现在非数组对象的属性值中时)
} else if (data[item] == data) {
// 规则5:对包含循环引用的对象(对象之间相互引用,形成无限循环)执行此方法,会抛出错误。
throw "cycling";
} else {
result.push(`"${item}":${jsonStringify(data[item])}`);
}
});
result = `{${result}}`;
}
}
return result;
}
# LazyMan
问题:
LazyMan("Hank");
// 输出:
// Hi! This is Hank!
LazyMan("Hank").sleep(3).eat("dinner");
// 输出:
// Hi! This is Hank!
// //等待3秒..
// Wake up after 3
// Eat dinner~
LazyMan("Hank").eat("dinner").eat("supper");
// 输出:
// Hi This is Hank!
// Eat dinner~
// Eat supper~
LazyMan("Hank").sleepFirst(2).eat("dinner").sleep(3).eat("supper");
// 输出:
// //等待2秒..
// Wake up after 2
// Hi This is Hank!
// Eat dinner~
// //等待3秒..
// Wake up after 2
// Eat supper~
// 以此类推
答案:
# 任务队列
class _LazyMan {
queue: any[] = [];
constructor(name: string) {
this.sayName(name);
setTimeout(() => {
this.next();
});
}
next() {
const fn = this.queue.shift();
fn && fn();
}
_holdOn(time) {
return () => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`Wake up after ${time} second`);
this.next();
}, time * 1000);
};
}
sayName(name) {
const fn = () => {
console.log(`Hi! This is ${name}!`);
this.next();
};
this.queue.push(fn);
}
sleep(time: number) {
this.queue.push(this._holdOn(time));
return this;
}
eat(some: string) {
const fn = () => {
console.log(`Eat ${some}~`);
this.next();
};
this.queue.push(fn);
return this;
}
sleepFirst(time: number) {
this.queue.unshift(this._holdOn(time));
return this;
}
}
const LazyMan = (name: string) => new _LazyMan(name);
LazyMan("Hank").sleepFirst(2).eat("dinner").sleep(3).eat("supper");
# 任务队列 + Promise 实现
class _LazyMan {
queue: any[] = [];
name: string;
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
this.sayName(name);
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
let sequence = Promise.resolve();
this.queue.forEach((item) => {
sequence = sequence.then(item);
});
});
}
sayName(name) {
this.queue.push(() => {
console.log(`Hi! this is ${name}!`);
});
return this;
}
eat(meal) {
this.queue.push(() => {
console.log(`eat ${meal}`);
});
return this;
}
_holdOn(time) {
return () =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`Wake up after ${time} second`);
resolve();
}, time * 1000);
});
}
sleep(time) {
this.queue.push(this._holdOn(time));
return this;
}
sleepFirst(time) {
this.queue.unshift(this._holdOn(time));
return this;
}
}
const LazyMan = (name: string) => new _LazyMan(name);
LazyMan("Hank").sleepFirst(2).eat("dinner").sleep(3).eat("supper");
export {};
// 参考文章:https://github.com/fi3ework/blog/issues/36
# 任务队列 + async 实现
class _LazyMan {
queue: any[] = [];
name: string;
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
this.sayName(name);
setTimeout(async () => {
for (let todo of this.queue) {
await todo();
}
// 下面这种写法也可以
// for await (let todo of this.queue) {
// todo()
// }
});
}
sayName(name) {
this.queue.push(() => {
console.log(`Hi! this is ${name}!`);
});
return this;
}
eat(meal) {
this.queue.push(() => {
console.log(`eat ${meal}`);
});
return this;
}
_holdOn(time) {
return () =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`Wake up after ${time} second`);
resolve();
}, time * 1000);
});
}
sleep(time) {
this.queue.push(this._holdOn(time));
return this;
}
sleepFirst(time) {
this.queue.unshift(this._holdOn(time));
return this;
}
}
const LazyMan = (name: string) => new _LazyMan(name);
LazyMan("Hank").sleepFirst(2).eat("dinner").sleep(3).eat("supper");
export {};
// 参考文章:https://github.com/fi3ework/blog/issues/36
# RxJS 实现
https://juejin.cn/post/6883706752487915534#heading-3 (opens new window)
# templateRender
// 就是把值从data里取出来
const render = (template, data) => {
return template.replace(/{{\s*?(\w+)\s*?}}/g, (match, key) => {
console.log(match, key);
return key && data.hasOwnProperty(key) ? data[key] : "";
});
};
const data = {
name: "神族九帝",
age: 100,
};
const template = `
我是: {{ name }}
年龄是: {{age}}
`;
console.log(render(template, data));
# list2tree
https://blog.shenzjd.com/pages/3fe27c66a9d72/#写一个函数-将以下数据结构转换成树形结构对象 (opens new window)
目标数组
// 目标数组
var arr = [
{ id: 3, parent: 2 },
{ id: 1, parent: null },
{ id: 2, parent: 1 },
];
期望结果
var obj = {
id: 1,
parent: null,
child: {
id: 2,
parent: 1,
child: {
id: 3,
parent: 2,
},
},
};
# 链表
function list2tree(list) {
let temp = {};
let root;
list.map((item) => {
if (item.prent === null) {
root = item;
}
temp[item.id] = item;
});
list.map((item) => {
if (temp[item.parent]) {
temp[item.parent].child = item;
}
});
return root;
}
# 找爸爸
function list2tree(list) {
const findParent = (child) => {
list.map((item) => {
if (item.id === child.parent) {
item.child = child;
}
});
};
list.map((item) => {
if (item.parent) {
findParent(item);
}
});
return list.find((item) => item.parent === null);
}
# 找儿子
function list2tree(list) {
const rec = (list) => {
list.map((parent) => {
list.map((item) => {
if (parent.id === item.parent) {
parent.child = item;
}
});
if (parent.child) {
rec([parent.child]);
}
});
};
rec(list);
return list.find((item) => item.parent === null);
}
# sleep
const sleep = (func, delay) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(func());
}, delay);
});
};
const consoleStr = (str) => {
return () => {
console.log(str);
return str;
};
};
const doFns = async () => {
const name = await sleep(consoleStr("神族九帝"), 1000);
const sex = await sleep(consoleStr("boy"), 1000);
const age = await sleep(consoleStr(100), 1000);
console.log(name, sex, age);
};
doFns();
# sum
/**
*
sum(1, 2, 3).valueOf() // 6
sum(2, 3)(2).valueOf() // 7
sum(1)(2)(3)(4).valueOf() //10
sum(2)(4, 1)(2).valueOf() //9
*/
const sum = (...args) => {
const add = (...args2) => {
args = [...args, ...args2];
return add;
};
add.valueOf = () => args.reduce((ret, num) => ret + num, 0);
return add;
};
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3).valueOf());
console.log(sum(2, 3)(2).valueOf());
console.log(sum(1)(2)(3)(4).valueOf());
console.log(sum(2)(4, 1)(2).valueOf());
# koa-compose
let middleware = [];
middleware.push((next) => {
console.log(1);
next();
console.log(1.1);
});
middleware.push((next) => {
console.log(2);
next();
console.log(2.1);
});
middleware.push((next) => {
console.log(3);
next();
console.log(3.1);
});
function compose(middlewares) {
let index = 0;
const rfn = () => {
if (index >= middlewares.length) return;
const middleware = middlewares[index];
index++;
return middleware(rfn);
};
return rfn;
}
console.log(compose(middleware)());
# 斐波那契数列
斐波那契数列是一个非常经典的数学问题,其中每一个数都是前两个数之和,例如:0、1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34……
F(0)=0,F(1)=1,F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)(n>=2,n∈N*)
在js中可以用递归,迭代,动态规划等方法实现。
// 定义如下:F(0)=0,F(1)=1,F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)(n>=2,n∈N*)
function fibonacci(n) {
// code here
}
// 验证
fibonacci(0)
fibonacci(1)
fibonacci(2)
fibonacci(3)
fibonacci(4)
# 递归
递归虽然简单,但是效率很低,时间复杂度为O(2^n),空间复杂度为O(n)。
function fibonacci(n) {
if(n < 2) return n;
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
# 迭代
迭代效率比递归高,时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1)。
function fibonacci(n) {
if(n < 2) return n;
let pre = 0;
let cur = 1;
let temp;
for(let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
[pre, cur] = [cur, pre + cur];
// pre = cur;
// temp = pre + cur;
// cur = temp;
}
return cur;
}
# 动态规划
动态规划是一种空间换时间的算法,时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(n)。
function fibonacci(n) {
if(n < 2) return n;
let dp = [0, 1];
for(let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}
# 矩阵快速幂
斐波那契数列的矩阵形式为:
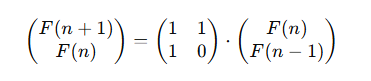 因此,我们可以通过快速幂算法来计算$F(n)$。时间复杂度为O(log n),空间复杂度为O(1)。
因此,我们可以通过快速幂算法来计算$F(n)$。时间复杂度为O(log n),空间复杂度为O(1)。
// 斐波那契转移矩阵乘法运算函数
function matrixMultiply(A, B) {
return [
[A[0][0] * B[0][0] + A[0][1] * B[1][0], A[0][0] * B[0][1] + A[0][1] * B[1][1]],
[A[1][0] * B[0][0] + A[1][1] * B[1][0], A[1][0] * B[0][1] + A[1][1] * B[1][1]]
];
}
// 斐波那契转移矩阵快速幂运算函数
function matrixPower(M, n) {
let result = [[1, 0], [0, 1]]; // 单位矩阵
let base = M;
while (n > 0) {
if (n % 2 === 1) {
result = matrixMultiply(result, base);
}
base = matrixMultiply(base, base);
n = Math.floor(n / 2);
}
return result;
}
function fibonacci(n) {
if (n === 0) return 0;
if (n === 1) return 1;
const F = [[1, 1], [1, 0]]; // 斐波那契转移矩阵
const resultMatrix = matrixPower(F, n - 1);
return resultMatrix[0][0]; // F(n) 就是矩阵的 [0][0] 元素
}
console.log(fibonacci(10)); // 输出斐波那契数列的第10项
# 比较不同的实现方式
递归方法的优点是代码简洁,容易理解,但缺点是在n很大的时候,递归调用层次过多,会导致堆栈溢出。另外时间复杂度比较高,为O(2^n),效率低。
迭代方法的优点是效率高,时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1),而且避免了递归带来的堆栈溢出问题。
动态规划方法的优点是效率高,时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(n)。但是相比于迭代方法,它需要额外的存储空间来保存中间结果。
矩阵快速幂方法的优点是效率非常高,时间复杂度为O(log n),空间复杂度为O(1)。但是它的实现比较复杂。
